Analog vs Digital Signals: Key Differences Explained
In the fast-evolving world of technology, the terms analog signals and digital signals frequently appear. Understanding these signal types is essential for anyone diving into telecommunications, electronics, or even everyday devices like smartphones and radios. This article offers a detailed yet easy-to-follow explanation, ensuring you walk away with clarity and answers to all your questions.
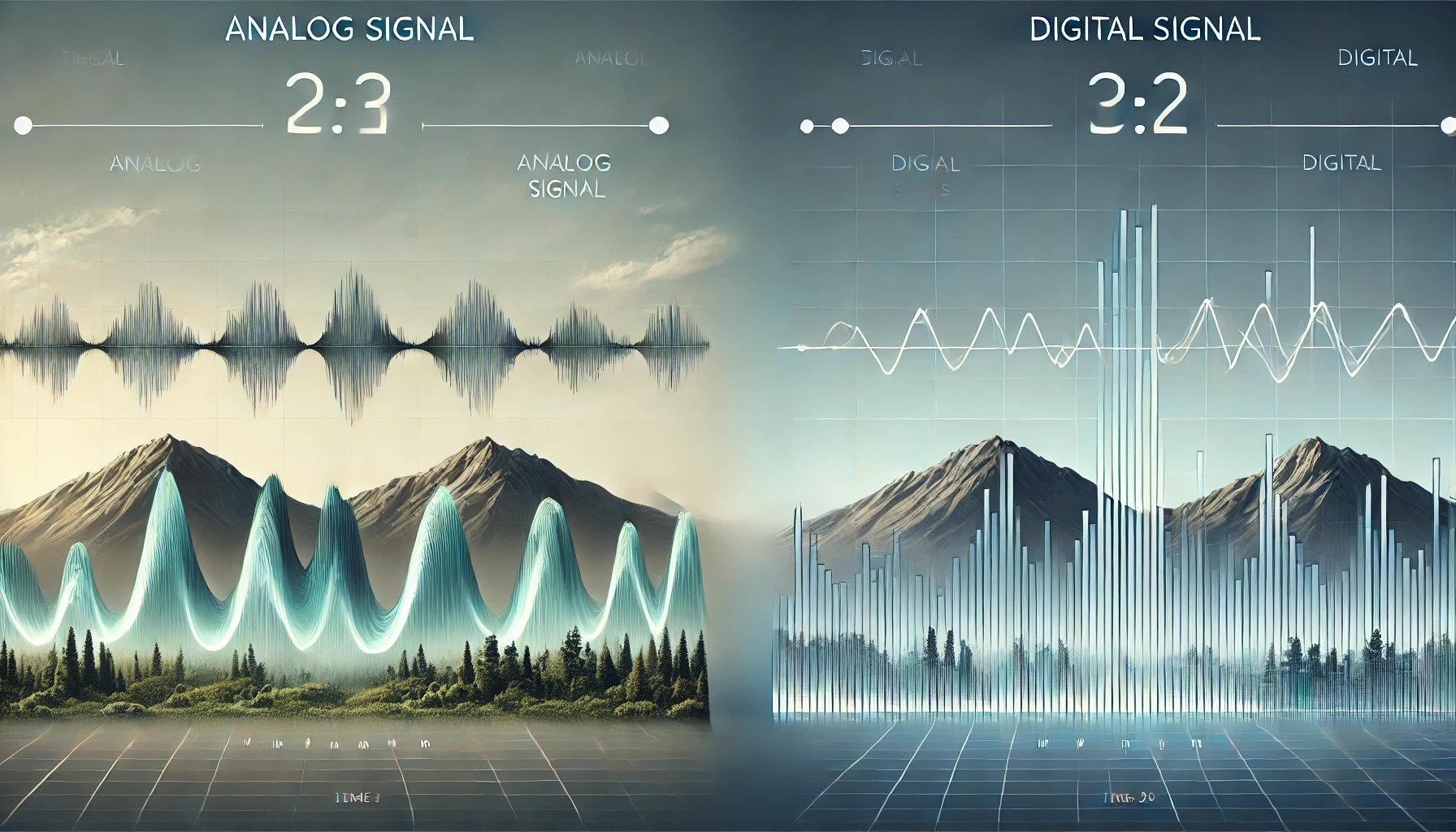
What Are Analog Signals?
Analog signals are continuous waveforms that naturally vary over time. They mimic real-world phenomena, such as sound waves or light intensity, and are represented by smooth, uninterrupted changes in amplitude or frequency.
- Key Examples: AM/FM radios, vinyl records, traditional telephones.
- Applications: Audio systems, analog TVs, and medical equipment like ECGs.
Key Features of Analog Signals:
- Continuity: Analog signals have no breaks or steps; they flow naturally.
- Real-World Representation: They closely resemble natural signals, making them ideal for capturing audio and visual data.
- Noise Sensitivity: Analog signals are prone to interference, which can distort their quality.
What Are Digital Signals?
Digital signals, in contrast, represent information using discrete values (usually binary: 0s and 1s). They offer greater reliability and efficiency in modern systems.
- Key Examples: CDs, DVDs, digital telephones, and streaming platforms.
- Applications: Internet communications, mobile phones, and digital audio systems.
Key Features of Digital Signals:
- Discrete Nature: Information is encoded in steps, allowing for precise representation.
- Error Correction: Built-in mechanisms ensure accuracy even in noisy environments.
- Ease of Storage and Transmission: Digital signals can be stored compactly and transmitted without loss.
Analog vs Digital Signals: A Detailed Comparison
| Aspect | Analog Signals | Digital Signals |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Continuous waveforms | Discrete binary pulses |
| Quality Over Distance | Degrades with noise | Maintains quality due to error correction |
| Processing | Requires analog systems for processing | Easily processed by computers and devices |
| Storage | Physical formats (e.g., tapes, records) | Digital files (e.g., MP3s, MP4s, cloud) |
| Applications | Older systems like analog radios | Modern systems like smartphones and IoT devices |
Advantages of Analog Signals
- Natural Sound Quality: Captures the richness of real-world sounds, making it ideal for audio enthusiasts.
- Cost-Effective for Simple Systems: Analog equipment is often cheaper for basic applications.
- No Conversion Needed: No digital-to-analog conversion is required for direct sound or light replication.
Advantages of Digital Signals
- Noise Immunity: Digital signals are less prone to degradation, ensuring consistent quality over long distances.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ideal for modern applications like streaming and cloud computing.
- Data Security: Digital systems enable encryption, offering enhanced security during transmission.
Practical Applications: When to Use Which?
Analog Signals:
- Audio Systems: Analog sound is richer for high-fidelity music setups.
- Medical Monitoring: ECG and EEG systems use analog signals for accuracy.
- Simple Communication: Analog radios are still used in remote or low-tech areas.
Digital Signals:
- Streaming Services: Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify rely on digital encoding for seamless delivery.
- Modern Telecommunication: Smartphones and 5G networks exclusively use digital signals.
- Smart Home Devices: IoT gadgets rely on digital signals for efficiency and integration.
Why Digital Signals Are Dominating Today
The transition from analog to digital systems is driven by the need for reliability, scalability, and precision. Digital signals enable technologies like:
- 5G Networks for faster internet speeds.
- AI and Machine Learning for advanced computing.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for immersive experiences.
While analog systems still have niche applications, the future is undoubtedly digital.
Common Questions About Analog and Digital Signals
- Why are digital signals better than analog? Digital signals are more resistant to noise, easier to store, and more secure.
- Can analog signals be converted to digital? Yes, through Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs), commonly found in microphones and cameras.
- What is the main disadvantage of digital signals? Digital systems require more complex technology and can lose natural quality during conversion.
- Are analog signals still used today? Absolutely! Analog signals are still vital in areas like radio broadcasting and medical imaging.
Final Thoughts: Which Is Right for You?
The choice between analog and digital signals depends on your needs:
- For Rich, Natural Sound: Choose analog systems.
- For Reliability and Modern Features: Digital systems are your best bet.
Whether you’re setting up a home audio system, exploring telecommunication technologies, or just curious, this guide provides all the insights you need.