Introduction
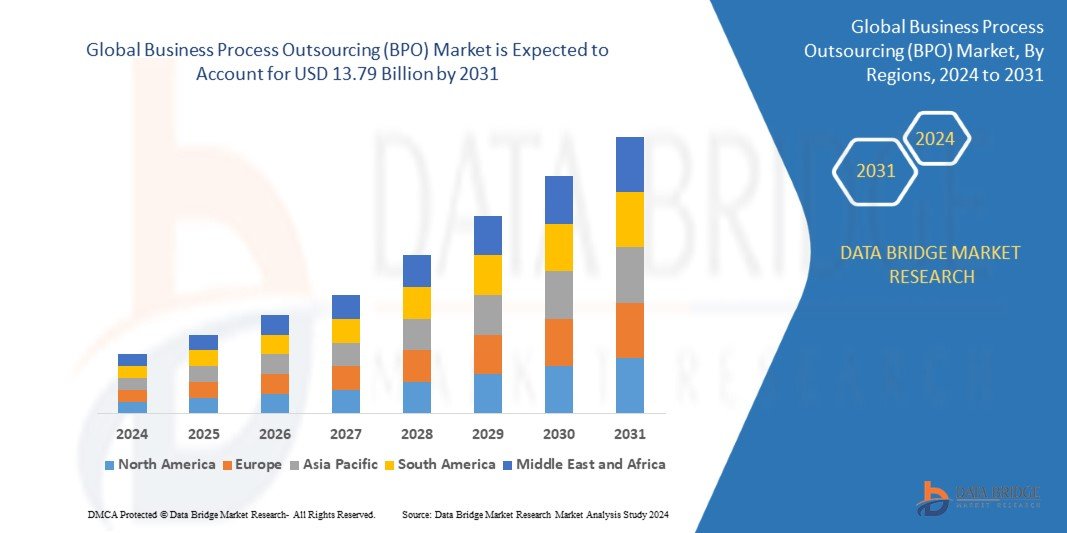
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) has emerged as one of the most significant business strategies in the modern global economy. By outsourcing various non-core processes to external providers, companies can focus on their primary competencies, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and scale their operations more effectively. BPO services range from customer support, payroll, and human resources to IT services, finance, and back-office operations.
Over the past few decades, the BPO industry has evolved into a multi-billion-dollar sector, driven by advances in technology, globalization, and the need for businesses to remain competitive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. This blog explores the concept of BPO, its types, benefits, trends, and how it is transforming the way businesses operate today.
What is Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)?
Business Process Outsourcing refers to the practice of contracting specific business functions or processes to a third-party provider. These processes can be categorized as front-office or back-office tasks:
- Front-office functions include customer-facing activities such as customer support, technical assistance, and sales.
- Back-office functions involve administrative and operational tasks such as accounting, data entry, payroll, and human resources.
By outsourcing these tasks, companies can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain access to specialized expertise. BPO allows businesses to focus on their core activities, such as product development, strategy, and customer relationships, while leaving non-core processes in the hands of experienced providers.
Types of Business Process Outsourcing
BPO can be broadly classified into different categories based on the type of services provided and the geographical location of the service provider.
1. Offshore BPO
Offshore BPO involves outsourcing business processes to providers in other countries, often to leverage lower labor costs and access specialized skills. Popular offshore destinations include countries like India, the Philippines, and Eastern European nations.
2. Nearshore BPO
In nearshore BPO, companies outsource their processes to providers in neighboring countries, usually in the same or similar time zones. This allows for easier communication and collaboration while still benefiting from lower costs. For instance, U.S. companies may nearshore to Mexico or Canada.
3. Onshore BPO
Onshore BPO involves outsourcing services to providers within the same country. Companies opt for onshore BPO when they prioritize local expertise, regulatory compliance, or real-time communication, despite potentially higher costs compared to offshore options.
4. Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)
A specialized subset of BPO, KPO involves outsourcing tasks that require advanced analytical and technical skills, such as market research, financial analysis, legal services, and engineering design. KPO services are often provided by highly skilled professionals and focus on delivering knowledge-based solutions rather than basic process tasks.
5. Information Technology Outsourcing (ITO)
Information Technology Outsourcing is a segment of BPO that focuses specifically on IT-related services. This includes application development, IT infrastructure management, technical support, cloud services, and cybersecurity solutions. ITO providers handle a wide range of technical processes to help businesses manage their IT requirements effectively.
Benefits of Business Process Outsourcing
BPO offers a range of benefits to organizations, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes and across various industries. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the primary drivers of BPO is cost savings. By outsourcing processes to regions with lower labor costs, companies can significantly reduce their operational expenses. BPO providers often operate in economies of scale, offering services at a fraction of the cost of maintaining in-house teams.
2. Focus on Core Competencies
Outsourcing non-core functions allows businesses to focus on their primary strengths and core activities, such as product development, marketing, and strategy. This focus helps companies stay competitive and innovative in their respective industries.
3. Access to Specialized Expertise
BPO providers typically have expertise in specific areas, offering specialized knowledge and skills that might not be available in-house. For example, outsourcing IT services to a specialized provider ensures that a company receives high-quality technical support and infrastructure management.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
BPO allows companies to scale their operations up or down based on their current needs. Whether it’s expanding customer support during peak seasons or reducing workforce during quieter periods, outsourcing offers the flexibility to adjust resources quickly.
5. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
BPO providers are often equipped with advanced technologies and best practices that streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance productivity. Businesses can benefit from faster turnaround times, improved service levels, and enhanced process automation.
6. Risk Management
Outsourcing certain business functions can help mitigate risks. For example, by entrusting IT services to a BPO provider, companies can ensure their data is securely managed and protected from cyber threats. Additionally, outsourcing helps companies navigate regulatory complexities by relying on experts who understand compliance requirements.
Key Industries Leveraging BPO
BPO services are utilized by a wide range of industries, each benefiting from the flexibility and expertise that outsourcing offers. Some of the key sectors that rely heavily on BPO include:
1. Healthcare
Healthcare organizations outsource processes such as medical billing, claims processing, and customer support to improve efficiency and reduce administrative burdens. With the rise of telehealth and digital health solutions, outsourcing IT and back-office functions has become even more critical for healthcare providers.
2. Banking and Finance
The financial services sector leverages BPO for tasks such as data processing, customer support, fraud detection, and compliance management. By outsourcing these functions, financial institutions can reduce operational costs while ensuring regulatory compliance and data security.
3. Retail and E-commerce
In the retail and e-commerce sectors, BPO providers handle customer support, order processing, inventory management, and logistics. By outsourcing these processes, retailers can focus on expanding their product offerings and improving customer experiences.
4. Telecommunications
Telecom companies outsource customer service, technical support, billing, and network management to specialized BPO providers. Outsourcing allows telecom firms to manage large volumes of customer interactions while maintaining service quality and reducing costs.
5. Information Technology
The IT industry is a significant user of BPO services, particularly for software development, technical support, infrastructure management, and cybersecurity. Outsourcing these tasks allows IT companies to focus on innovation and new product development while ensuring high-quality service delivery.
Trends Shaping the Future of BPO
As technology evolves and business demands shift, the BPO industry is undergoing significant transformation. Several key trends are shaping the future of BPO:
1. Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The rise of automation and AI is revolutionizing BPO services. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-powered tools are increasingly being used to handle repetitive, rule-based tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and improving efficiency. AI chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming commonplace in customer service roles, providing quick and accurate responses to customer inquiries.
2. Cloud-Based Services
With the shift to cloud computing, BPO providers are increasingly offering cloud-based solutions to enhance flexibility and scalability. Cloud services enable seamless data access, improved collaboration, and reduced infrastructure costs for businesses relying on BPO services.
3. Data Security and Privacy
As companies outsource more processes, data security and privacy concerns are becoming paramount. The implementation of regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) has placed a greater emphasis on protecting sensitive information. BPO providers are investing in advanced cybersecurity measures to ensure compliance and safeguard their clients’ data.
4. Omnichannel Customer Support
With the increasing use of digital channels, companies are focusing on delivering omnichannel customer support, where customers can interact with businesses via phone, email, chat, social media, and more. BPO providers are enhancing their capabilities to offer seamless, integrated support across multiple platforms, ensuring consistent customer experiences.
5. Focus on Sustainability
As businesses become more environmentally conscious, there is growing pressure on BPO providers to adopt sustainable practices. Outsourcing partners are now focusing on reducing their carbon footprint by implementing energy-efficient technologies, minimizing waste, and supporting remote work to reduce travel-related emissions.
Challenges in BPO
Despite its many benefits, BPO is not without its challenges. Some of the key challenges businesses face when outsourcing include:
1. Quality Control
Maintaining consistent quality across outsourced processes can be difficult, particularly when dealing with offshore providers. Clear communication, defined service-level agreements (SLAs), and regular monitoring are essential to ensure quality standards are met.
2. Data Security Concerns
Outsourcing processes that involve sensitive information, such as customer data or financial records, can raise data security concerns. Businesses must ensure their BPO partners have robust security protocols in place to protect against breaches and unauthorized access.
3. Cultural and Language Barriers
When outsourcing to offshore providers, cultural and language differences can sometimes hinder effective communication and collaboration. Choosing providers with strong language skills and cultural alignment is important to avoid misunderstandings.
4. Hidden Costs
While BPO can offer significant cost savings, there can be hidden costs associated with managing the outsourcing relationship, such as travel expenses, legal fees, and additional management overhead.
How to Choose the Right BPO Provider
Selecting the right BPO provider is crucial to the success of your outsourcing strategy. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for providers with a proven track record in your industry and expertise in the specific processes you want to outsource.
- Technology and Innovation: Ensure the provider uses modern technologies, such as automation, cloud-based solutions, and AI, to enhance efficiency and deliver better outcomes.
- Security and Compliance: Verify that the provider adheres to industry-standard security protocols and complies with relevant regulations, especially if handling sensitive data.
- Communication and Collaboration: Choose a provider with strong communication skills and a collaborative approach to ensure smooth interactions and alignment with your business goals.
- Cost Transparency: Look for providers that offer clear pricing structures and transparency in all cost-related aspects of the outsourcing partnership.
Conclusion
Business Process Outsourcing has become a vital strategy for companies seeking to streamline operations, reduce costs, and stay competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape. As technology continues to evolve and the global economy becomes more interconnected, BPO will remain an essential tool for businesses looking to improve efficiency, access specialized expertise, and scale their operations.
By understanding the various types of BPO, its benefits, and the emerging trends shaping the industry, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting the right outsourcing partner and building a successful outsourcing strategy for the future.